| Introduction | Alprazolam, often sold under the brand names of Xanax, Alp, Neuxam, Praz and others, is a short-acting tranquilizer that belongs to the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which consists of benzodiazepines (BZDs) fused with a triazole ring. It’s most typically used to treat anxiety disorders in the short term, such as panic disorder or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) |
| Class of Medicine | Alprazolam is a benzodiazepine (a medicine that has a relaxing, tranquil effect). It works by reducing aberrant brain excitation. |
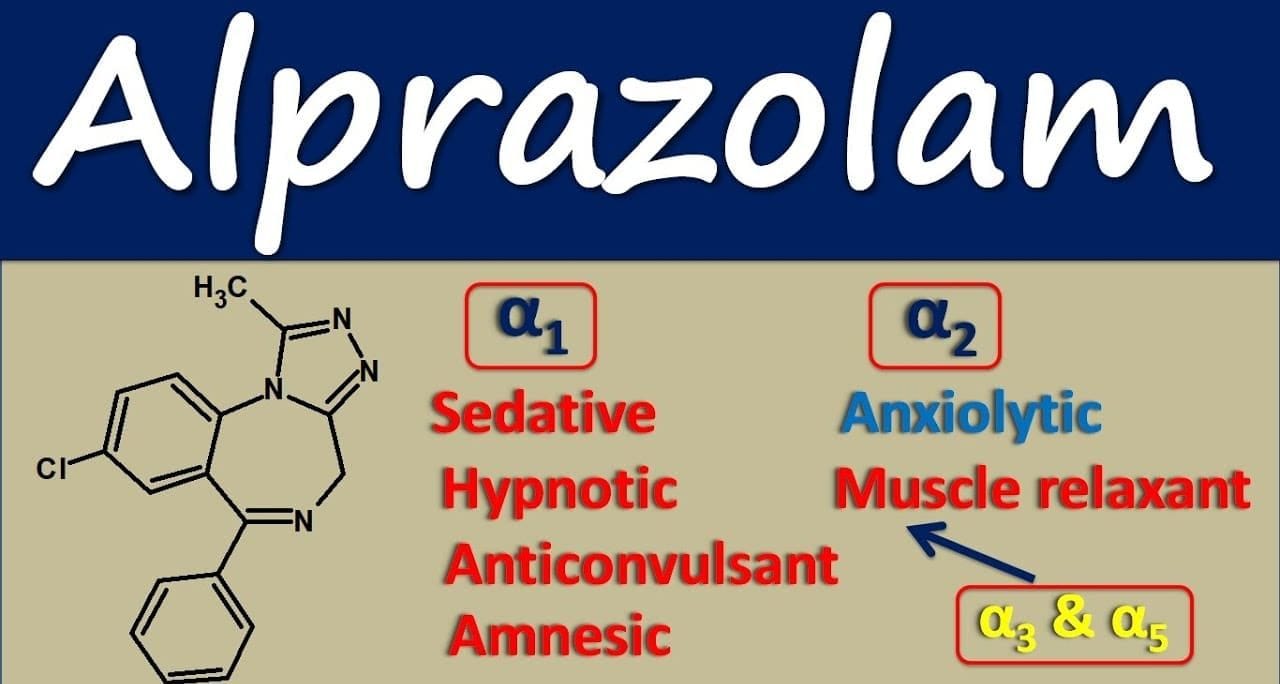
| Mode of Action | Alprazolam works by attaching to a specific location on the central nervous system’s gamma-aminobutyric acid A (GABAA) receptor. The receptor’s affinity for the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA is increased as a result of this binding action. GABA activity is increased, which inhibits the transmission of neuronal signals in the brain that cause anxiety and panic. |
| Medical Uses | Alprazolam is primarily used for the short-term treatment of anxiety disorders, (sudden, unexpected attacks of extreme fear and worry about these attacks), panic disorders, and chemotherapy-induced nausea. Alprazolam may also be prescribed for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder and anxiety disorders that are accompanied by depression. The FDA recommends that the physician evaluate the drug’s usefulness on a regular basis. |
| Avaiability & Usage | Alprazolam is available in tablet form. Alprazolam can be taken on a daily basis at set times or as needed (“PRN”). Your healthcare practitioner will usually limit the amount of dosages you can take in a single day. Alprazolam is a potent benzodiazepine that should only be used for six weeks at a time. |
| Side Effects | Commeon side effects includes: Sleepiness Depression Headaches Fatigue Dry mouth Memory issues Some of the sedation and exhaustion may subside after a few days. |
| Important Warning | Don’t take alprazolam without consulting your physician. When used with other drugs, alprazolam can cause significant or life-threatening respiratory issues, drowsiness, or coma. So inform your physician about the medication you already taking. |
| Available Brands | Xanax Alp Neuxam Praz |




