No products in the cart.
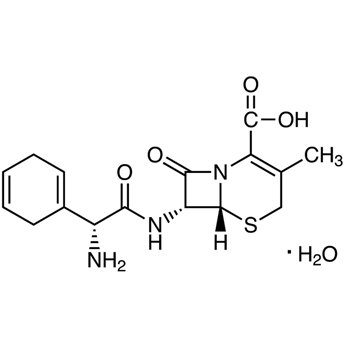
Cefradine is a cephalosporin antibiotic that is used to treat various bacterial infections. It is available in capsule form, and is also known by its brand name, Velosef. Cefradine capsules are prescribed by doctors to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and more.