No products in the cart.
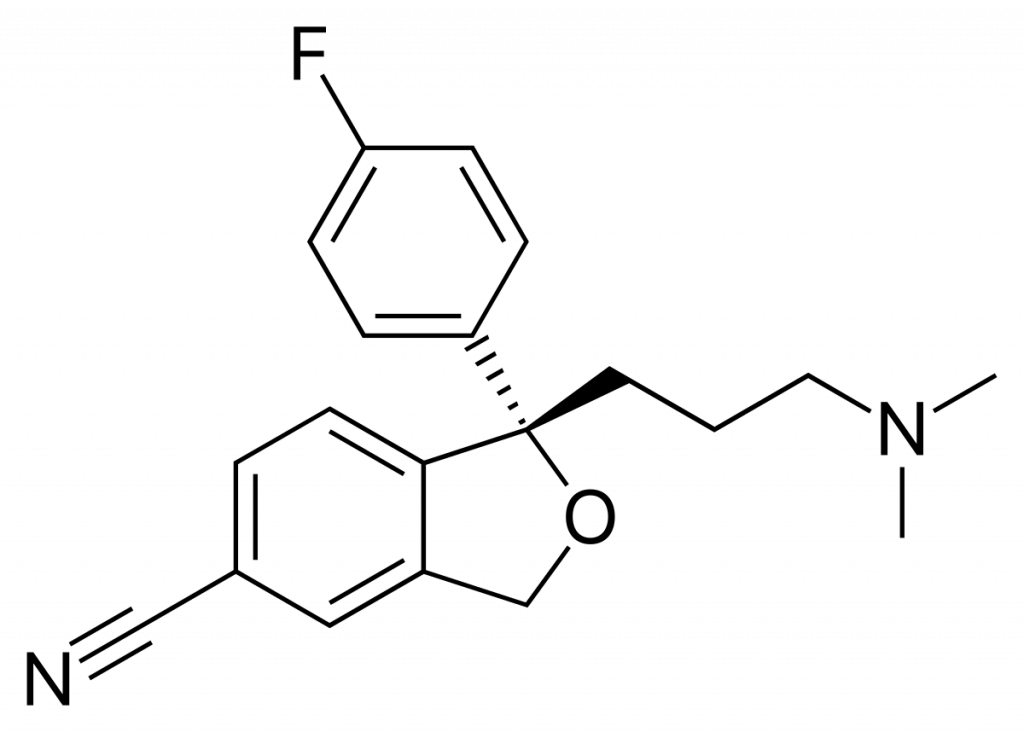
Escitalopram is an antidepressant and anxiety medication, available in oral tablet or liquid form under the brand names of Cipralex, Citanew, Es-Pramcit, Excita. It works by assisting in the restoration of a natural substance (serotonin) equilibrium in the brain.