No products in the cart.
Methylcobalamin – Mecobalamin – Vitamin B12
Introduction
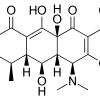
Methylcobalamin (mecobalamin, MeCbl, or MeB12) available in the brand names of Methycobal, Cobalmin, Mabil, Neuromet and others, is a kind of vitamin B12 known as cobalamin. Vitamin B12 insufficiency is treated with methylcobalamin. Vitamin B12 is required for the proper functioning of the brain and nerves, as well as the synthesis of red blood cells.
Methylcobalamin is also used to treat peripheral neuropathy, diabetic neuropathy, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis as a preliminary treatment.
Pernicious anaemia, diabetes, and other diseases may necessitate the usage of methylcobalamin.
Class of Medicine
Mecobalamin and Methylcobalmin are two terms that are interchangeable and both belong to the vitamin B12 family (cyanocobalamin and analogues). Vitamin B12 insufficiency is treated with this supplement (Anemia). Vitamin B12 is required for the proper functioning of the brain and nerves, as well as the synthesis of red blood cells. In persons with pernicious anaemia, diabetes, and other diseases, methylcobalamin is sometimes used.
Mode of Action
Ingested methylcobalamin is first transformed to cob(II)alamin by MMACHC before being employed as a cofactor. Cob(II)alamin is then transformed into adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin, which are then used as cofactors. To put it another way, methylcobalamin is first dealkylated, then regenerated.
Treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency using hydroxocobalamin, cyanocobalamin, or a mix of adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin, rather than methylcobalamin alone, is critical.
How should this medicine be used?
Methycobalamin, often known as mecobalamin, is available in tablet, capsule, and injection form. Water-soluble vitamins are better absorbed when eaten on an empty stomach, which is the optimal way to eat. That means bringing them in for the first time in the morning, 30 minutes before eating, or two hours after eating. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water and are used by your body.
It could be injected every day or on alternate days when using injections.
Common Side Effects
Some of the common side effects of Methylcobalamin are:
Nausea
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Loss of appetite
Headache
Important Warning
Methylcobalamin can cause blood clots, diarrhoea, paresthesia, rhinitis, ataxia, pruritis, and allergic responses at high doses. Before starting this therapy, people with polycythemia should talk to their doctor [26-29]. This medication can be used as a topical paste on the skin without causing any side effects. This drug’s intravenous infusion can cause hypersensitivity reactions, which can lead to anaphylactic shock. While using methylcobalamin to treat megaloblastic anaemia, hypokalamia and thrombocytosis have occurred in certain patients.
Available Brands (list can be updated in future)
Methycobal
Cobalmin
Mabil
Neuromet